Textile Reinforced Concrete Prototyping Technology (TRCPT) at CSIR-SERC
Textile Reinforced Concrete Prototyping Technology (TRCPT) at CSIR-SERC
CSIR-Structural Engineering Research Centre (CSIR-SERC), Chennai, one of the national laboratories under Council of Scientific & Industrial Research (CSIR), New Delhi, has developed pioneering technologies for producing various textile reinforced concrete (TRC) products.
Reinforced concrete (RC) is one of the most widely used building materials in the construction industry. One of the major disadvantages of RC, however, is that its steel reinforcement is prone to corrosion. Textile reinforced concrete (TRC) is an innovative composite material that is making rapid strides in the construction industry, across the globe.
Textile Reinforced Concrete Prototyping Technology (TRCPT) encompasses green and innovative construction practices that can be deployed to make products without using moulds. As per the industry assessment, TRCPT replicates the multi-vitamin concept in the construction sector, by facilitating production of both structural and non-structural precast products.
TRCPT developed at CSIR-SERC has been identified as one among the Top 100 Indian Innovation in the year 2022.
License Agreement was signed between CSIR-SERC and L&T Construction
License Agreement was signed between CSIR-SERC and L&T Construction
On the occasion of International Women's Day (8th March 2024), an License Agreement was signed between CSIR-SERC and L&T Construction – Water & Effluent Treatment IC, Chennai, in the presence of Director, CSIR-SERC, for transfer of technology titled “Textile Reinforced Concrete Prototyping Technology (TRCPT) ” . The technology was developed by Dr. (Mrs.) Smitha Gopinath, Principal Scientist. Mrs. Sakthi Chitra, Chief Engineering Manager, signed the license agreement on behalf of L&T.
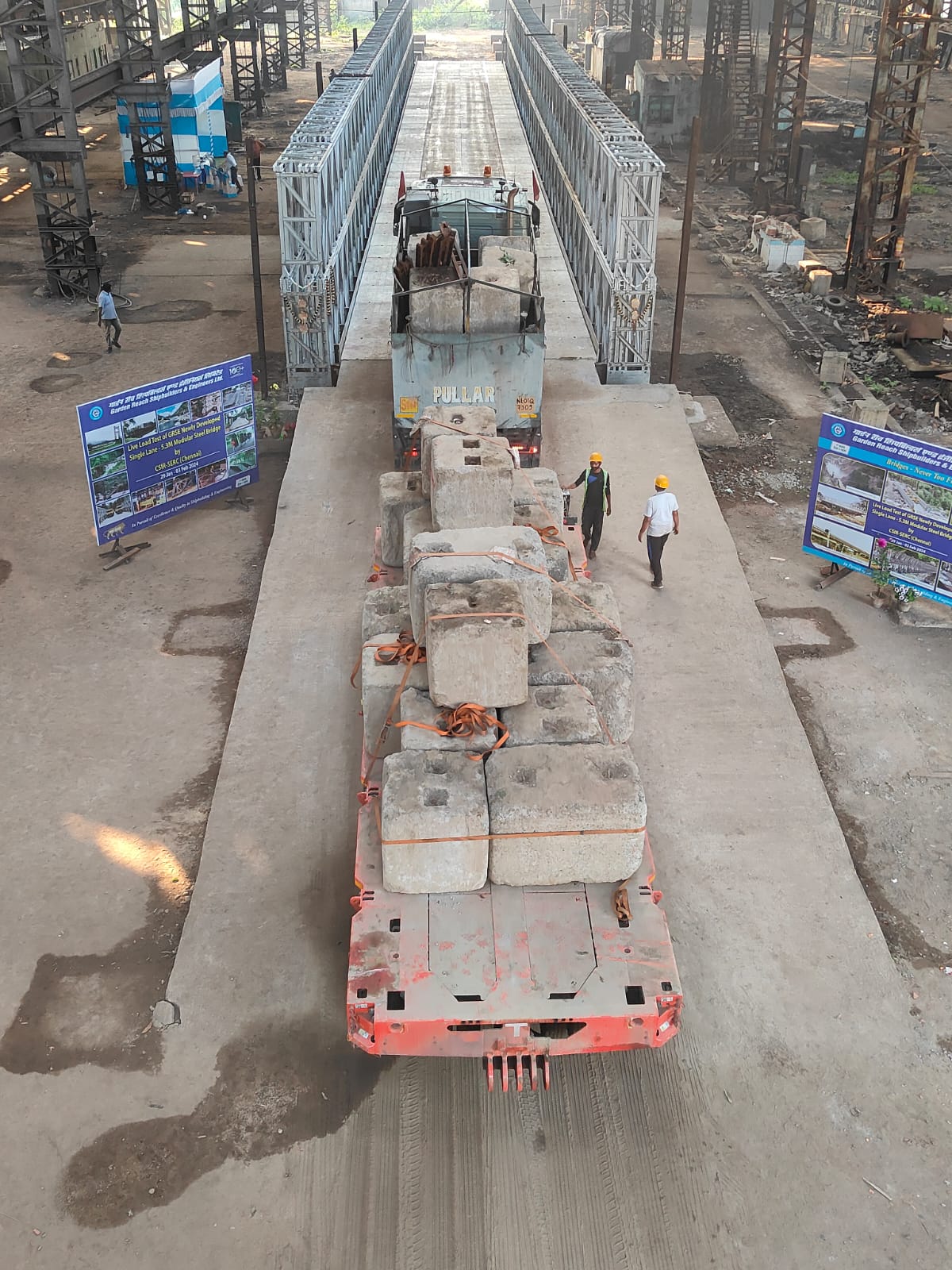
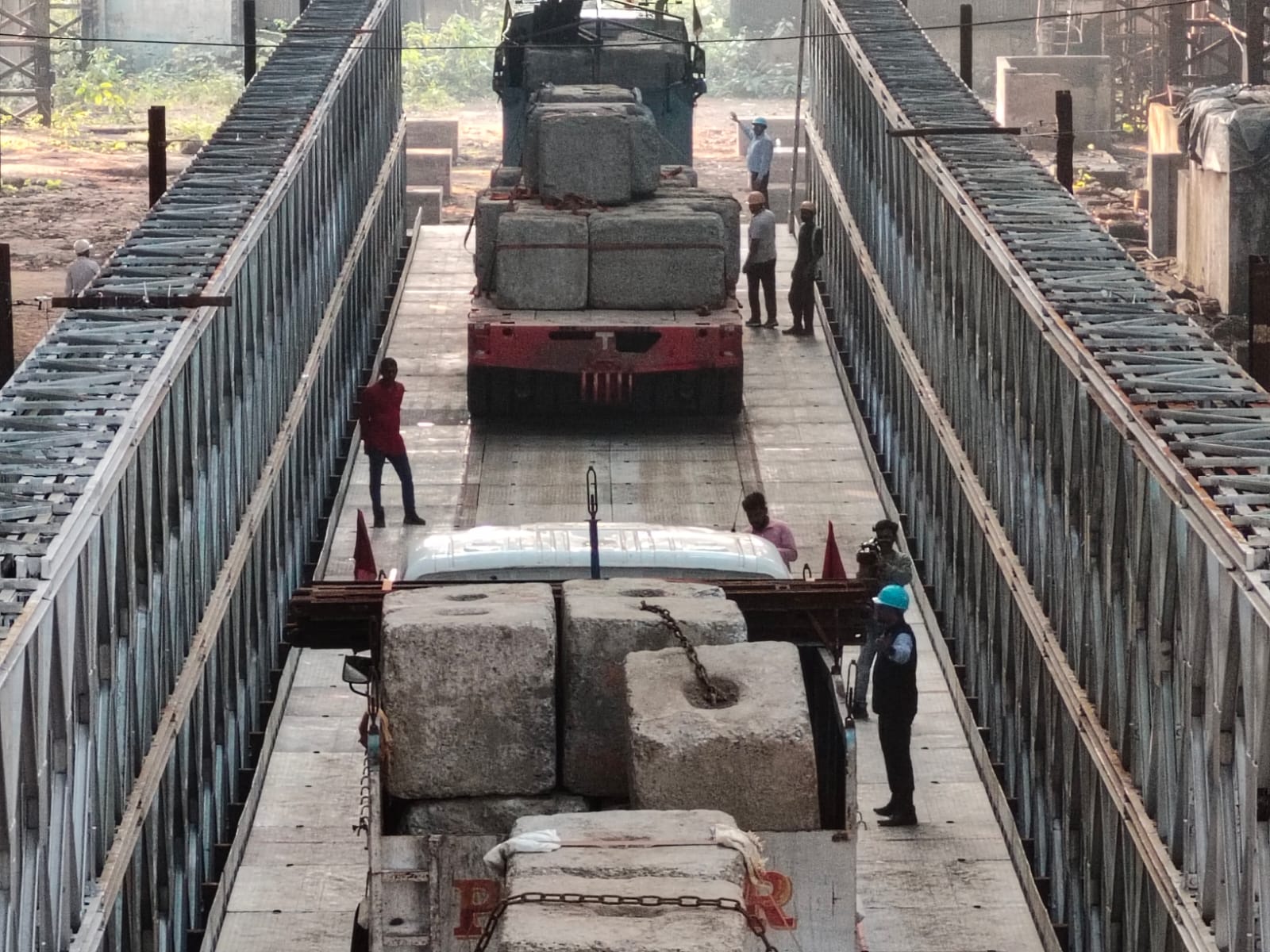
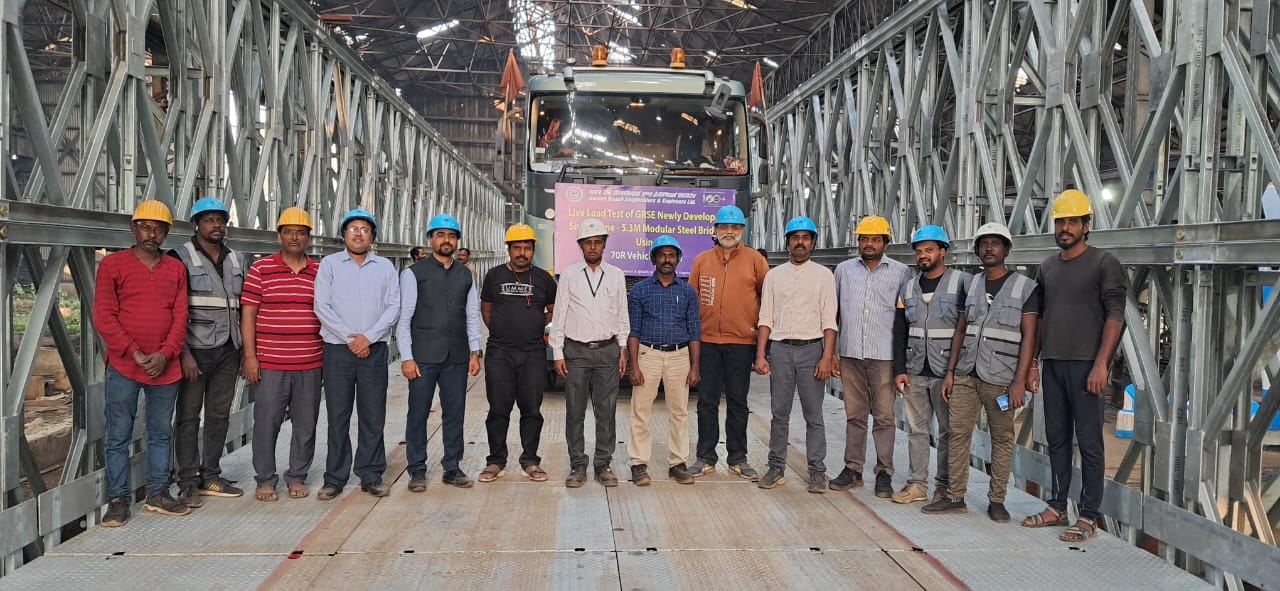
CSIR-SERC successfully completes load test of Modular Steel Bridge for GRSE
CSIR-SERC successfully completes load test of Modular Steel Bridge for GRSE
A modular steel bridge of 200 feet span and 5.3 m width was tested under 70R (100 tons of load) loading as per IRC-6 by CSIR-SERC for Garden Reach Shipbuilders, Kolkata on 1st and 2nd Feb 2024 at GRSE premises. Two nos of 70R loads were sequentially positioned on the bridge as per IRC-6. The bridge was extensively instrumented with strain gauges, LVDTs and dial gauges to measure the strains and deflections at critical locations. The test was successfully completed and the bridge passed the load test.
TRC boundary wall deployment in Delhi-Mumbai Expressway
Textile reinforced concrete fence developed at CSIR-SERC implemented in Delhi-Mumbai Expressway
CSIR-Structural Engineering Research Centre, Chennai, has developed cost effective and easy to implement textile reinforced concrete (TRC) panels for fence and boundary wall constructions. TRC consists of fine grained cementitious binder and indigenous alkali resistant glass textile as reinforcement. TRC fence have advantages such as: durability, light weight, easy production at site and in factories, precast nature, easy transportability etc. TRC fence being a novel product in Indian market, its use will help to enhance the technical textile production in India. The scope of such fencing panels also further opens up customization of walling solutions for kinds of infra projects needs like right of way (ROW) wall fence for high ways, railway projects, solar power project boundary walls & SEZ land boundary walls and also for Border management fencing in various regions in our country.
The implementation of TRC fence at site is simpler and is done as a panel to post insertion. Panel length ranging from 1m to 2.4 m have been developed for site implementation. No heavy machineries are required for production or implementation of the proposed TRC fence panels. Compared to the conventionally used fence at present using precast concrete and prestressed concrete, the proposed folded TRC panels provides reduction in material cost, transportation cost, cement consumption, and weight for fence and boundary wall applications. In addition, textile reinforced concrete has the unique advantage of being non-corrosive as well. The minimal maintenance, reduce construction time and risk, reduced material usage, reduce life cycle cost, and sustainable construction are the benefits of using TRC boundary walls.
“Textile reinforced concrete fence technology for boundary wall applications" developed at CSIR-SERC, Chennai, has been licensed to L&T Construction (Transportation Infrastructure IC), Mumbai, on a non-exclusive basis. A trial stretch of 70m has been deployed near Ratlam in Delhi-Vadodara expressway project package by L&T, Mumbai.
Completion of Indo-German project “CleanWater” funded by IGSTC at CSIR-SERC
Modular lightweight wastewater treatment units made with TRC for rural and periurban dwelligns (CleanWater)
Within the Indo-German project “CleanWater”, project consortia consisting of CSIR-Structural Engineering Research Centre (CSIR-SERC), Chennai; IITMadras, Chennai; Raina Industries Private Limited (Mumbai); Institute of TextileTechnology (ITA) at RWTH Aachen University , Germany; and Betonwerk Hentschel GmbH, Elsterwerda developed a resource-efficient solution for enabling wastewater treatment in rural and peri-urban regions using modular and decentralised textile reinforced concrete waste water treatment plant.
The application of non-corrosive textile-reinforced concrete (TRC) as construction material opened up new opportunities of lightweight construction and the conserving of resources. Their use in wastewater treatment plants allows less maintenance and enhanced durability compared to conventional construction materials. In the project, Textile specifications were developed by ITA RWTH; characterisation and durability studies on TRC have been conducted at IITMadras; Numerical modelling, structural design and testing was carried out at CSIR-SERC; site deployment was done by Raina Industries. The TRC decentralized wastewater treatment modular units of 2.4m3 capacity developed in the project can be for the use in remote and rural regions and shall be transported to the communities for implementation on site. One such implementation has been completed in Samata Vidyalaya, Pune, Maharashtra, on 6th Oct 2023, through which 1000 students will be the beneficiaries. Further, due to lightweight nature of the material TRC, it significantly facilitates the transport and implementation without use of any heavy-duty equipment.
The entire team of the “CleanWater” project thank the DST (Department of Science and Technology, Government of India) for funding and the coordination of the “CleanWater” research project within the Indo-German Science & Technology Centre (IGSTC) and the BMBF (Federal Ministry of Education and Research), Germany, the DLR Projektträger, Germany.
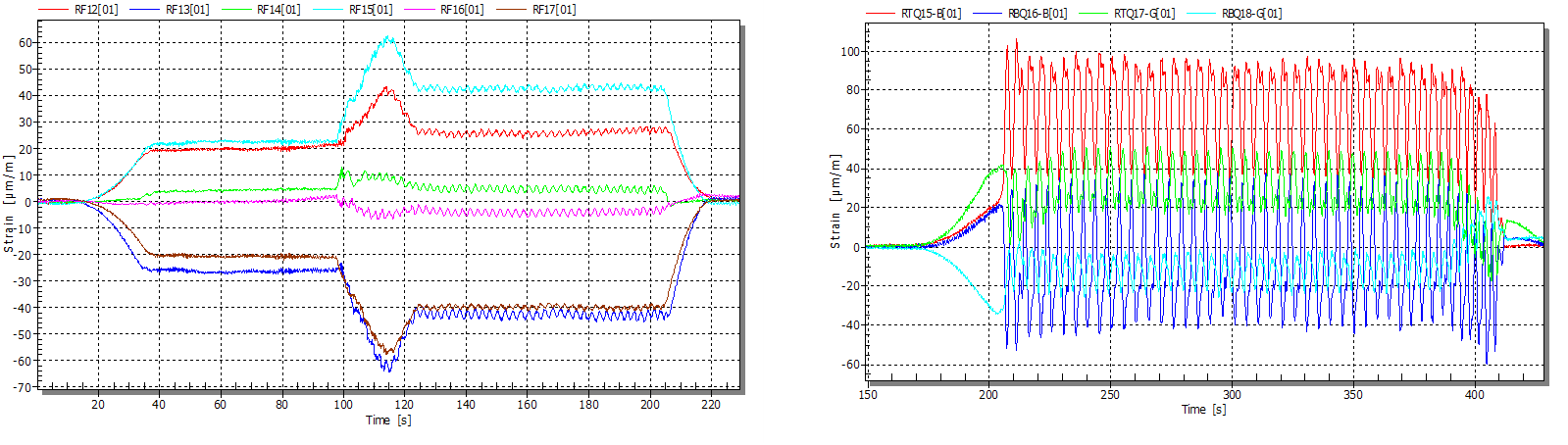
Evaluation of performance of J P Setu, 2nd longest rail-road bridge over river Ganga at Patna and formulation of damage mitigation strategies based on dynamic response measurements using...
Evaluation of performance of J P Setu, 2nd longest rail-road bridge over river Ganga at Patna and formulation of damage mitigation strategies based on dynamic response measurements using...
Jai Prakash Narayan Setu Bridge (JP Setu, Br No.7) across river Ganga at Patna is the second longest rail-road bridge which was commissioned to service in the year 2016. However, the bridge started showing distress in some of the joints and the pot...
Jai Prakash Narayan Setu Bridge (JP Setu, Br No.7) across river Ganga at Patna is the second longest rail-road bridge which was commissioned to service in the year 2016. However, the bridge started showing distress in some of the joints and the pot bearing supports over the period of service. East Central Railway has entrusted CSIR-SERC for complete investigation on few typical spans of the bridge through instrumentation, dynamic testing and numerical simulation studies to study on the cause of distress and for retrofitting of the bridge. The total length of the bridge is around 4.5km having 36 numbers of 123m spans of simply supported through truss girders having rail at the bottom deck level and roadway at the top deck. Three numbers of typical spans of the bridge were identified for investigation, and comprehensive instrumentation scheme for measuring the deflection, strains on various members, vibration and rotation of the supporting pot bearing was formulated. The bridge spans were completely instrumented and tested with two fully loaded complete test train formations for various static and dynamic test case scenarios in single and opposite direction of running trains. This type of testing is first time adopted to get the complete understanding of the bridge behaviour under operating train running conditions. Exhaustive numerical simulation studies were carried out simulating the dynamic test running cases of the train formations using vehicle-track-bridge interaction models. Based on the investigations carried out, report will be submitted to ECR detailing on the investigations carried out, distress assessment, and retrofitting strategies to be adopted for briging the bridge to its full service stage conditions of designed loading and speeds.
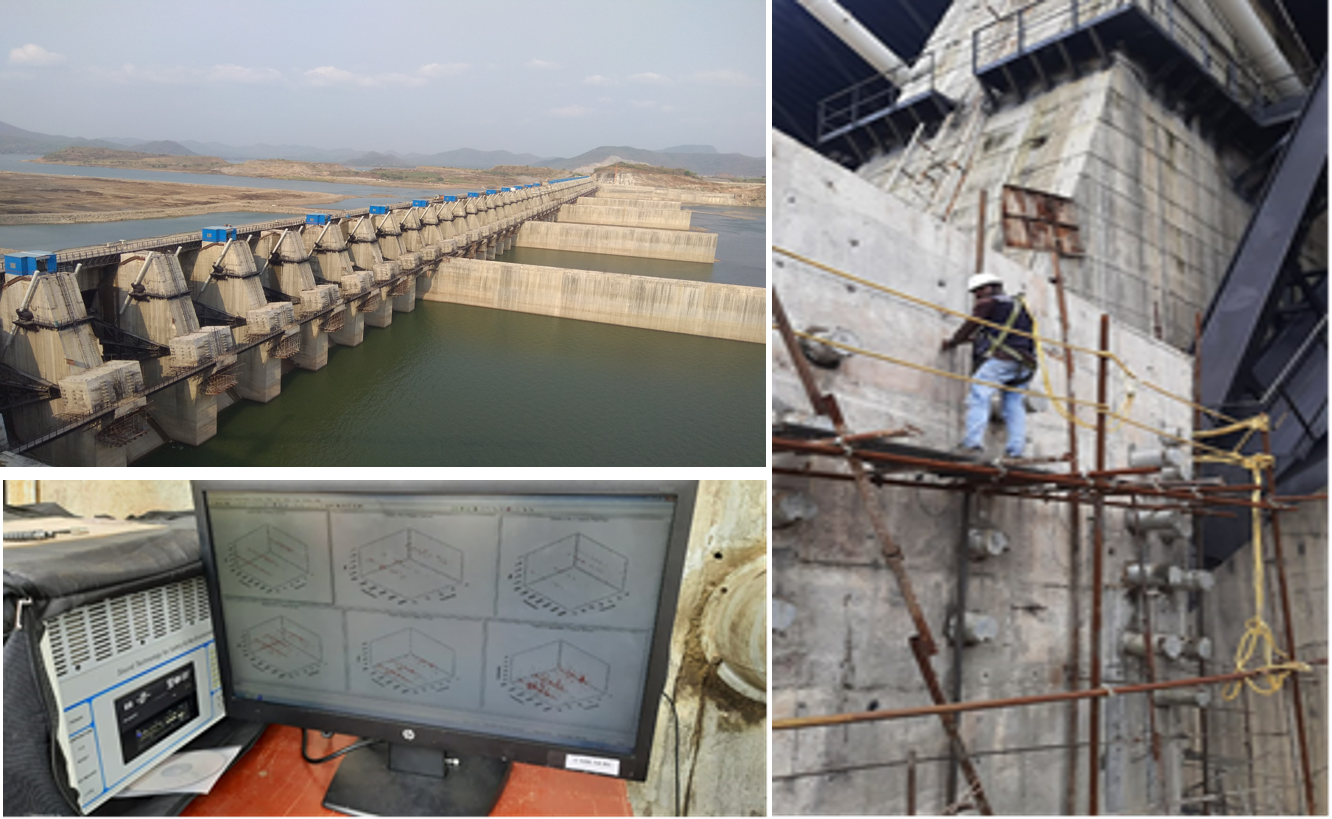
Integrity assessment of the prestressed Trunnion beams of the spillway structure of Polavaram dam project through Acoustic Emission (AE) and advanced non-destructive evaluation (NDE) Techniques
Integrity assessment of the prestressed Trunnion beams of the spillway structure of Polavaram dam project through Acoustic Emission (AE) and advanced non-destructive evaluation (NDE) Techniques
Polavaram dam project, one the most prestigious and challenging national projects in India is located on river Godavari near Ramayyapet village of Polavaram Mandal of West Godavari district in Andhra Pradesh.
Polavaram dam project, one the most prestigious and challenging national projects in India is located on river Godavari near Ramayyapet village of Polavaram Mandal of West Godavari district in Andhra Pradesh. This is a multipurpose major terminal reservoir project for the development of Irrigation, Hydro power and drinking water facilities to East Godavari, Vishakhapatnam, West Godavari and Krishna districts of Andhra Pradesh. The span of the dam is about 1.2 km, having a pier height of 54 m and a total of 48 radial gates (16mx20m) which are connected with 49 prestressed Trunnion Beams (5.5mx5.5m section and length varied from 9.5m to 16m depending on the location of the trunion). In order to assess the integrity of the prestressed Trunnion beams of the spillway structure of the dam, Polavaram Irrigation Project, Head Works Circle (PIPHW), Dowlaiswaram, East Godavari District, Andhra Pradesh, entrusted a project to CSIR-SERC for integrity assessment by conducting series of different Acoustic Emission (AE) and advanced non-destructive evaluation (NDE) tests on all the 49 trunnion beams. The challenge is to identify the presence of flaws/discontinuities inside concrete where the conventional NDT&E methods are not applicable due to massive size, high amount of reinforcement bars near surface concrete, presence of prestressing duct, cable and grout, and possibilities of flaws well inside the concrete surface.
A comprehensive and multi-point AE technique was used for the first time, to the specific task of investigating health of the trunnion beams. During the investigations, slow movement of the radial gates and high-speed acquisition of data through multi-channel were carried out using integrated and synchronized AE System. Using the AE parameters, existing flaws/discontinuities, if any, are identified through intensive signal processing. In order to assess the integrity, number of AE hits, signal amplitude and signal strength are considered.
Figure: Integrity assessment of prestressed trunnion beams in Polavaram Dam using Acoustic Emission (AE) technique by CSIR-SERC team
Condition Assessment of RCC Structures of Tapovan Vishnugad Hydro Power Project (4 X 130 Mw) affected by Unprecedented Massive Glacial Debris Flow
Condition Assessment of RCC Structures of Tapovan Vishnugad Hydro Power Project (4 X 130 Mw) affected by Unprecedented Massive Glacial Debris Flow
National Thermal Power Corporation (NTPC) is constructing a 520 MW hydro-electric power plant located downstream on the Alaknanda River at Tapovan, Joshimath, Uttarakhand. For this power plant, a dam is under construction across the Dhauliganga...
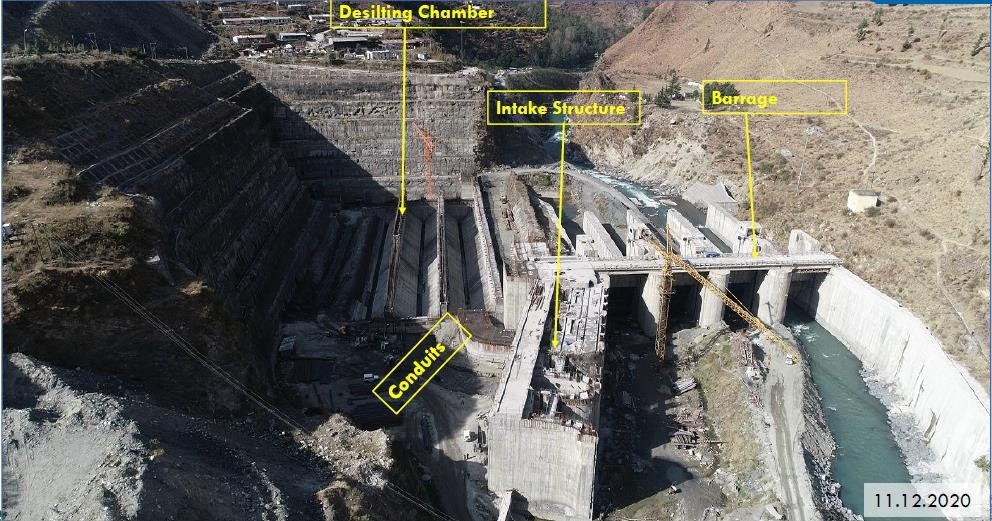
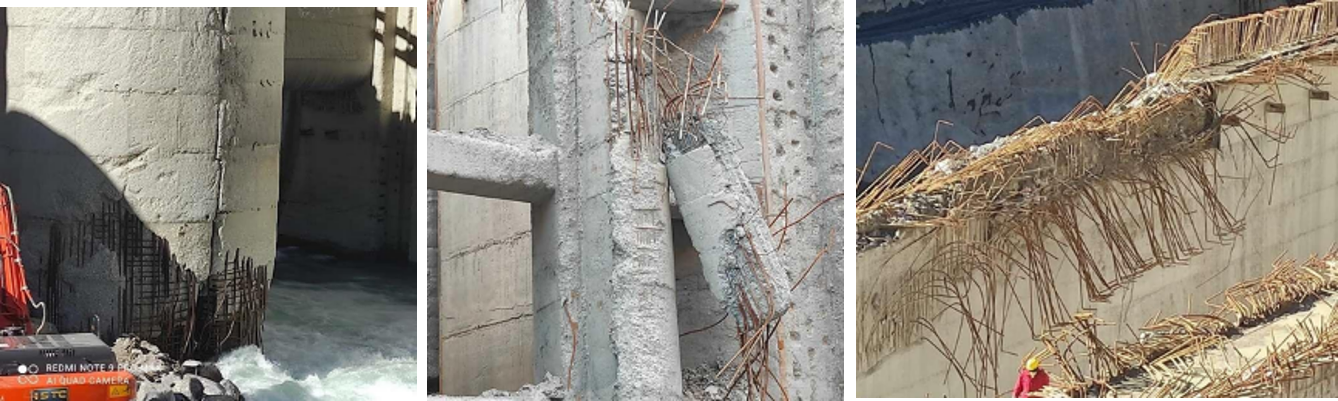
National Thermal Power Corporation (NTPC) is constructing a 520 MW hydro-electric power plant located downstream on the Alaknanda River at Tapovan, Joshimath, Uttarakhand. For this power plant, a dam is under construction across the Dhauliganga River with a catchment area of 3,100 km2. The dam main structure consists of barrage structure, intake structure, desilting structure, and tunneling. An unprecedented massive glacial debris flow occurred on 7th February 2021 and the subsequent devastating flood full of debris/silt/boulders/ice/rock pieces/soil/trees etc. flooded the barrage under-construction. Due to this natural disaster, all the dam structures were severely damaged and the bridge deck slabs, head operating rooms, and radial gates were washed away, one breast wall was completely sheared off, and the other breast walls were severely damaged.
The problem was referred to CSIR-SERC by NTPC to assess the condition of various dam structures including barrage, intake, and de-silting chambers, to have confidence for using the dam structure further.
CSIR-SERC took this challenging project of National Importance and carried out detailed scientific investigations on the dam structure consisting of (i) visual observation of dam structure, (ii) evaluation of concrete quality and integrity through NDT, (iii) ensuring the vertical and horizontal alignment through Total Station Survey, (iv) assessment of geological parameters, (v) providing quality assurance and quality control methodology, on war footing basis and provided appropriate remedial solutions to NTPC based on which the damaged dam structure of the Tapovan Vishnugad Hydro Power Project is being restored.
Fatigue strength evaluation of alumino thermit welded rail joints successfully done at CSIR-SERC
With a vast railway network crisscrossing the length and breadth of India, safety on tracks is of paramount importance. Long welded rails are used extensively in railway tracks in India for increasing the speed of the rolling stock and better travel...
With a vast railway network crisscrossing the length and breadth of India, safety on tracks is of paramount importance. Long welded rails are used extensively in railway tracks in India for increasing the speed of the rolling stock and better travel comfort. Fatigue fracture of rails is a possible occurrence in railway tracks because of the fluctuating stresses due to the varying traffic conditions and low fracture toughness of rail steels. Most rails are made from plain carbon steel to keep their cost low. Due to heat affected zone adjacent to the weld, fatigue becomes critical in welded joints.
Fatigue life evaluation of number of welded rail joints from government and private agencies are carried out at CSIR-Structural Engineering Research Centre (CSIR-SERC), Chennai, as per the specifications of the Research Designs & Standards Organisation (RDSO), Lucknow. The rail joints have to withstand two million cycles of constant amplitude sinusoidal cyclic loading. The test samples have an overall length of 2 m. They are supported over a span of 1.5 m and the load is applied at two points at a distance of 75 mm from the centre. Three samples have to be tested and all the three rail joints have to pass the specified number of cycles.
Such modern fatigue strength tests by CSIR-SERC are helping Indian Railways to ensure safety of rail tracks. CSIR-SERC has been in the forefront in assisting Indian Railways for the past three decades, in assessing the quality of welded rail joints. CSIR-SERC has recently successfully completed fatigue strength evaluation of alumino thermit welded rail joints for Indian Railways.
The alumino thermit process is extensively being used world over for joining the ends of the rails. Alumino thermit welding is a process that causes fusion of metals by heating them with superheated molten metal from an alumino thermit reaction between a metal oxide and aluminium. The significance of alumino thermit welding is that it is done at site.
RDSO Project
Evaluation, analytically as well as experimentally, the longitudinal force coming on the sub-structure of railway bridges.Formulation of guidelines for design provisions regarding longitudinal loads on steel and prestressed concrete bridges
Evaluation and Management of Longitudinal Force on Substructure of Railway Bridges
The objectives of this project are:
- Evaluation, analytically as well as experimentally, the longitudinal force coming on the sub-structure of railway bridges.
- Formulation of guidelines for design provisions regarding longitudinal loads on steel and prestressed concrete bridges
- Review and evaluation of suitable methodologies/techniques for mitigation of longitudinal forces.
- Training of 30 nos. RDSO/ Indian Railways officials and engineers for evaluation of longitudinal force on bridge sub structure and its mitigation.